Creating VM to RHV by Ansible
Written by Ilkka TengvallThis time I’d like to describe a handy way we have for creating a virtual machine into our lab. Normally in ITIL organisations it is something behind a slow ticket. We wanted to have demos for our work, and don’t want to repeat manually the steps to do basic tasks. Instead we want to quickly do by press of a button, within few minutes:
let’s look at the steps in Ansible
This play is executed in deploy_vm_rhv.yml playbook. Let’s break it into pieces.
Asking VM parameters
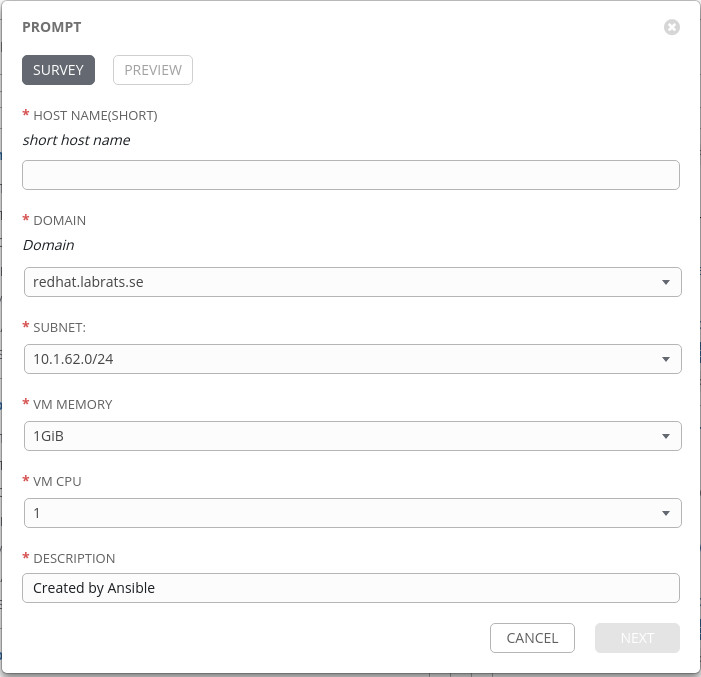
This step we do in Ansible Tower:
Load secrets from Ansible Vault
Next we want to load private information related to our lab from Ansible Vault. We store SSH key for automation, some passwords and other sensitive info there. Tower is set with vault password, so it can read secrets before execution of tasks.
tasks:
- name: Include secrets to be used
no_log: true
include_vars: secrets.yml
Get IP address from IPAM server
We want to have also IP addressing and name service automated. PhpIPAM is used to manage them. We use API to replace the network person’s secret excel sheet :) You’ve been warned!
- include_role:
name: ansible-role-phpipam-get-ip
vars:
phpipam_hostname: "{{ short_hostname + '.' + domain }}"
See ansible-role-phpipam-get-ip here.
RHV, please create VM for us
We have RHEL template in RHV. Creating such is topic for another blog. Ansible has ovirt modules which let’s us command RHV. You could substitute that with VMware modules, until you migrate it to RHV. There are lot of options available. We use standard RHEL KVM image from access portal. To customise it we utilise cloud-init to push in the credentials we want. Tower also feeds RHV the user and job ids for VM metadata, so we know who owns the machines.
- include_role:
name: ansible-role-rhv-vm
vars:
rhv_vm_name: "{{ short_hostname }}"
rhv_vm_domain: "{{ domain }}"
rhv_vm_ip: "{{ phpipam_ip }}"
rhv_vm_netmask: "{{ phpipam_netmask }}"
rhv_vm_gw: "{{ phpipam_gw }}"
rhv_vm_dns1: "{{ phpipam_nameserver1 }}"
rhv_vm_state: running
We want to do these configurations in the VM
Ansible waits for machine to boot up. Once it allows SSH login, we move on to do VM internal configurations
- include_role:
name: ansible-role-resolv-conf
- include_role:
name: ansible-role-satellite-bootstrap
- include_role:
name: ansible-role-date-time
- include_role:
name: ansible-role-ipa-client
- include_role:
name: ansible-role-nagios-nrpe
Configure name resolution
We have automation for our DNS. IdM will know all names of our machines. VM is set to listen to correct name servers (DNS). See ansible-role-resolv-conf here.
Register to satellite
Satellite keeps us up to date with latest software. Our VMs don’t pull install packages from internet, but they are cached locally in Satellite. See ansible-role-satellite-bootstrap.
Set time and date
We use chrony to keep time in sync. See ansible-role-date-time here.
Register to user management
Did you know that with your RHEL you get Red Hat identity management (IdM)? It works like AD controlling the users and groups. It adds SSH key management for users and servers also. This way we don’t need to push users separately to VMs, but their credentials and SSH keys are managed centrally. IdM is core piece for SSO technology for web apps too.
See ansible-role-ipa-client here.
Register to monitoring
At the end we add VM to Nagios monitoring. That sets our mind far from ease by bombing us with Telegram messages in case something is wrong in our lab :)
You probably have already some monitoring tool in use in you company. If so, just replace this part with your own module. See ansible-role-nagios-nrpe here.
We also tell Nagios server that there is a new client to monitor:
- include_role:
name: ansible-role-nagios-bootstrap
vars:
monitored_server: "{{ short_hostname + '.' + domain }}"
nagios_bootstrap_state: present
See ansible-role-nagios-bootstrap here.
VM is ready to serve in minutes!
ATM this is our procedure to bring up a VM in automated way. Ask us for more if you got interested. Remember, we put these out here to save your time on your job. They are free to use, go get them :)
About the credits, I wrote this blog, but majority of playbooks were written by Peter Gustafsson, who got loose. We just couldn’t hold him doing it, ansible is so great. Magnus Glanz sneaked to keyboard and added the Nagios parts. The rest of us caught the guys only at this phase, and will contribute also.
More about different steps about automation in following blogs, consider the ice broken with this first article! See you hopefully soon,
BR, ikke
I work as an SA at Red Hat Nordics, mainly with speeding things up using automation and hybrid cloud.
